Engine valve – precision control for marine and industrial engines
Engine valves are essential components in every combustion engine, ensuring precise control over intake and exhaust processes. Whether in marine engines, gas-powered generators, stationary industrial motors, or locomotive engines, the right engine valve ensures operational efficiency, combustion accuracy, and long service life. Choosing OEM-quality engine valve parts is critical for long-term performance, safety, and cost-efficiency.
What is an engine valve?
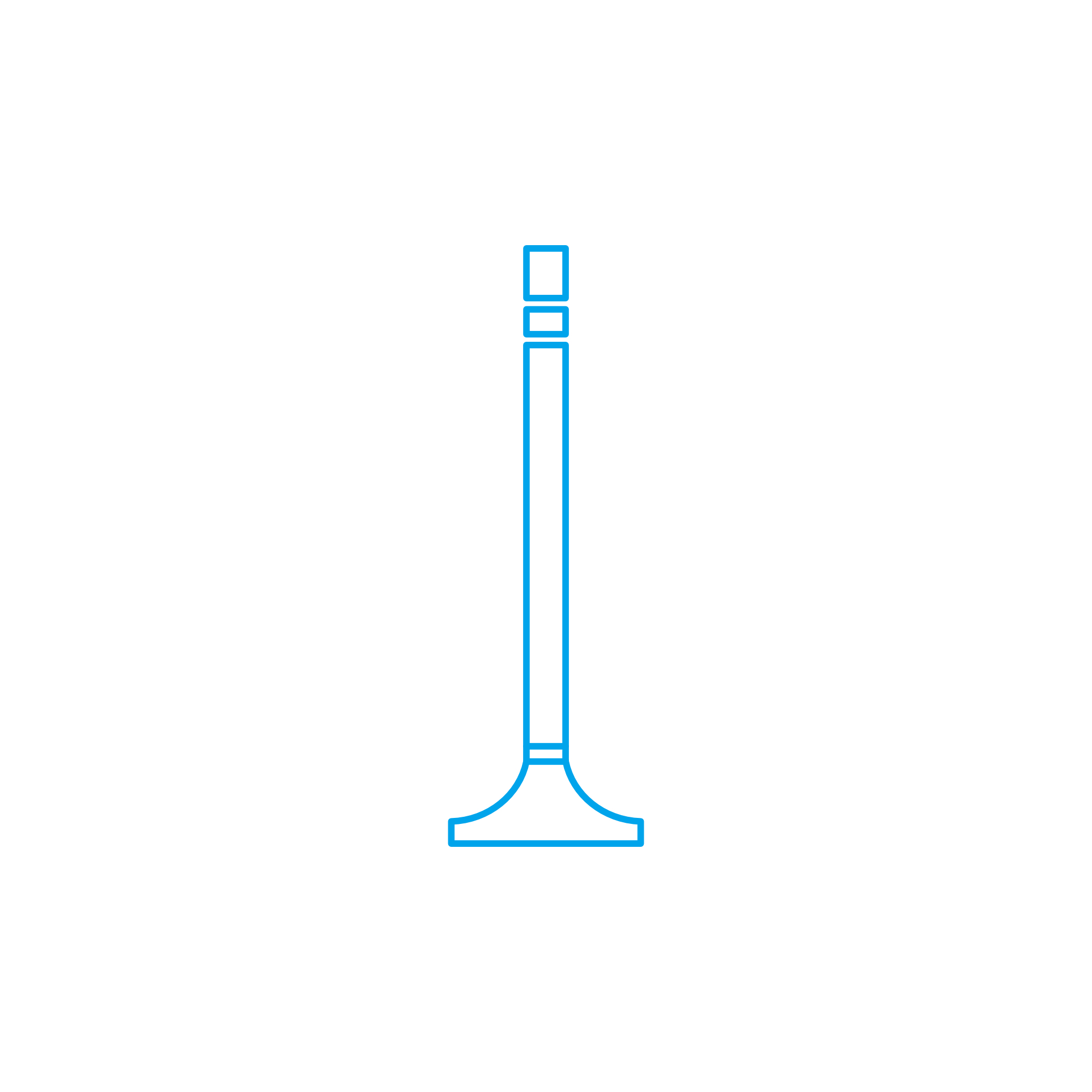
An engine valve is a mechanical component that opens and closes to control the flow of gases into and out of the engine cylinders. Typically made from heat-resistant metals, each valve for engine operation must withstand extreme temperatures and high-pressure environments.
There are two primary types: intake valves, which allow the air-fuel mixture to enter the combustion chamber, and exhaust valves, which release burned gases after combustion. The opening and closing cycles of these valves are precisely timed to the engine’s rotation, ensuring seamless combustion and power delivery.
Function and benefits of engine valves
The valves engines rely on must perform under extreme stress. The proper functioning of each valve of engine directly impacts power output, fuel efficiency, and emissions. Worn or faulty motor valves can lead to misfires, reduced engine performance, overheating, or even total engine failure.
Here are the key benefits of using high-quality engine valve parts:
- Optimized sealing and compression
- Efficient combustion and power delivery
- Extended engine life and maintenance intervals
- Reduced emissions and fuel consumption
- Enhanced thermal and mechanical durability
Types, materials and OEM compatibility
Depending on the application, engine valves differ in design and construction. Intake valves are optimized for cooler airflow, while exhaust valves endure hotter temperatures and aggressive gases. Materials range from hardened steel to titanium alloys, often with surface treatments like nitriding or chrome plating for added wear resistance.
Our engine valve parts meet strict OEM standards, ensuring full compatibility with a wide range of engine models. This includes precise dimensions, material specifications, and valve timing synchronization. Whether you're replacing a single motor valve or sourcing complete valves engines sets, our parts are engineered for lasting reliability and performance.
Use cases and industrial relevance
Engine valves play a central role in marine propulsion systems, stationary power units, gas engine installations, and locomotive drives. In these environments, any failure in the valve for engine functionality can cause severe operational downtime. That’s why OEM-compliant, technically precise engine valve parts are essential across all heavy-duty applications.
Buying advantages with us
We supply only OEM-grade motor valves and engine valve parts, ensuring a precise fit and high durability. With fast DHL Express delivery worldwide, technical customer support, and a wide selection tailored for marine and industrial engines, we help you keep operations running with confidence. Easy online ordering and multiple payment options make the procurement process efficient and secure.
Frequently asked questions about engine valves
What is an engine valve?
An engine valve controls the flow of air, fuel, and exhaust gases in a combustion engine. It opens and closes at precisely timed intervals, supporting efficient combustion and power output.
What are the parts of a engine valve?
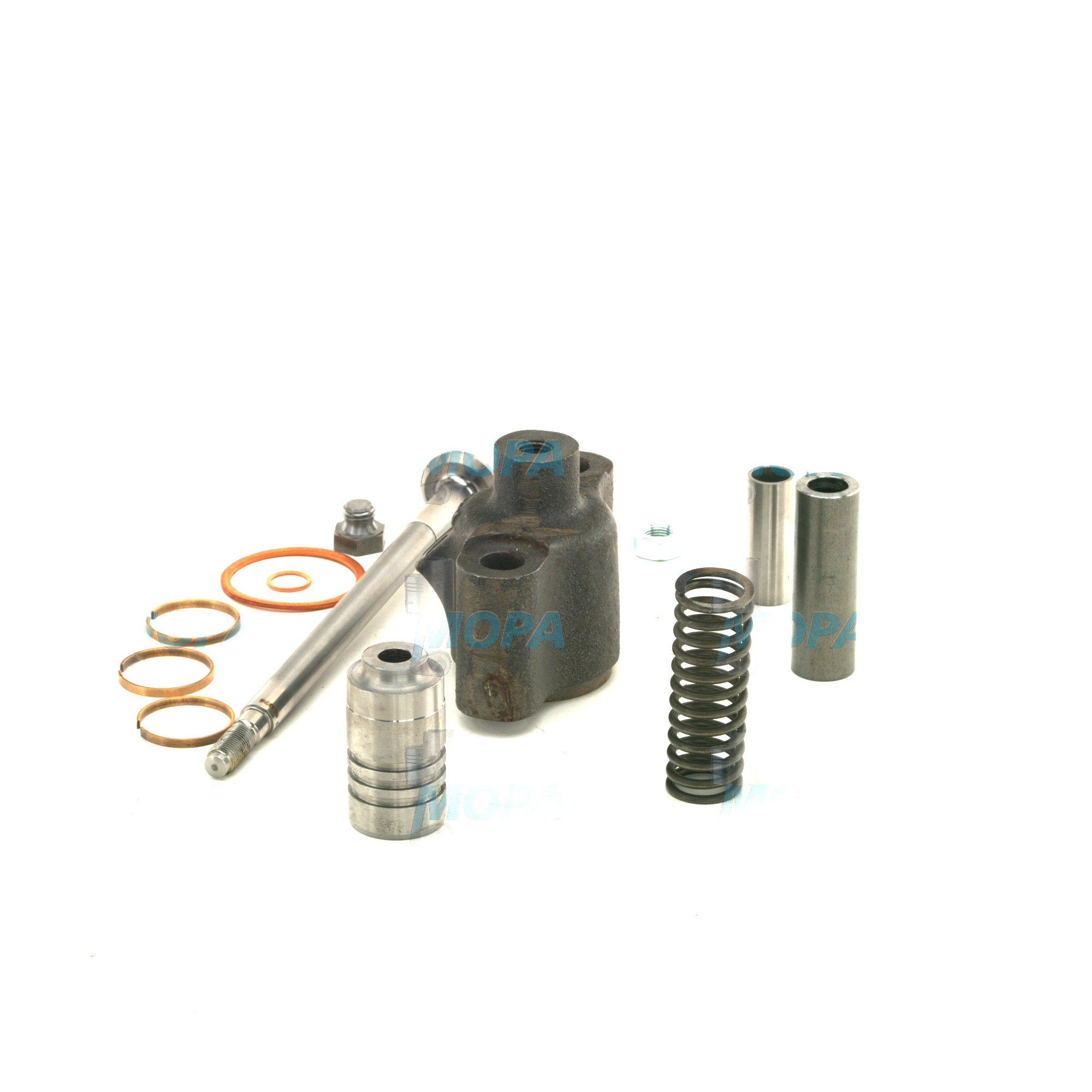
Typical parts of a engine valve include:
- Valve head (seals against the seat)
- Valve stem (guides the motion)
- Valve seat (provides the sealing surface)
- Spring and cotters (ensure return and retention)
- Guide (ensures proper alignment and reduces friction)
Related components for sealing and engine control
Engine valves operate in conjunction with other vital components such as gaskets, hoses, valve guides, springs, and cooling systems. These elements must work together to maintain compression, regulate temperature, and ensure overall engine stability—especially in demanding marine and industrial settings.